KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2025 Vol. 24Development of a nanoparticle supercrystal fabrication method using linker-mediated covalent bonding reactions
A method has been developed to fabricate highly stable gold nanoparticle supercrystals using linker-mediated covalent bonding reactions. This technique maintains structural stability under various environmental conditions and allows for size control, indicating broad potential applications for supercrystals.
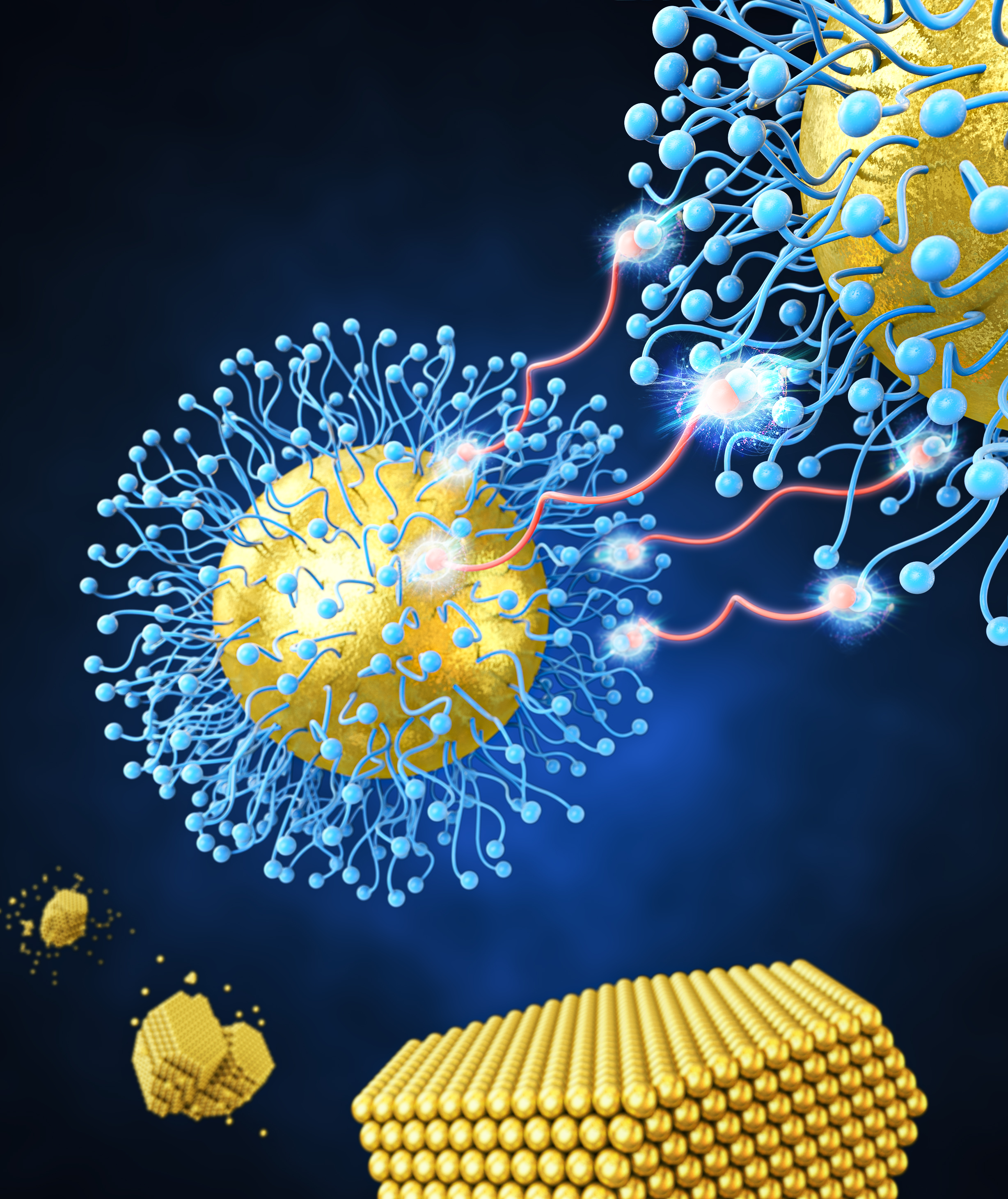
Ensuring the structural stability of nanoparticle supercrystals is essential for their use in a wide range of potential applications. The Neutron Scattering and Nanoscale Materials Laboratory led by Professor Sung-min Choiin the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering has successfully developed a method to fabricate highly stable gold nanoparticle supercrystals using linker-mediated covalent bonding reactions. Adipic acid was employed as a linker molecule, and esterification reactions in the presence of H₂SO₄ connected gold nanoparticles functionalized with 6-mercaptohexanol to form supercrystals.
The resulting gold nanoparticle supercrystals predominantly exhibited face-centered cubic (fcc) Wulff polyhedra structures with a uniform size distribution. Moreover, the supercrystals maintained their structural stability under various conditions, including solvents with different polarities and pH values (0–14), drying environments, and temperatures up to 175°C.
The formation process of the nanoparticle supercrystals involves random uniform nucleation during growth, a gradual shift from reaction-controlled to diffusion-controlled growth modes over time, and the oriented attachment of smaller crystals. This fabrication method also allows for precise size control of the nanoparticle supercrystals by adjusting the concentration of the linker molecules and the reaction temperature. The excellence of this research was recognized, and it was published as a cover article in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters in June 2024.
Most Popular

When and why do graph neural networks become powerful?
Read more
Smart Warnings: LLM-enabled personalized driver assistance
Read more
Extending the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries with water
Read more
Professor Ki-Uk Kyung’s research team develops soft shape-morphing actuator capable of rapid 3D transformations
Read more
Oxynizer: Non-electric oxygen generator for developing countries
Read more