KAIST
BREAKTHROUGHS
Research Webzine of the KAIST College of Engineering since 2014
Spring 2025 Vol. 24Deep Learning Networks for Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge (BRATS)
MRI Laboratory at KAIST wins first prize among 2200 worldwide participating teams in 2021 Brain Tumor Segmentation (BRATS) Challenge co-hosted by three international societies (RSNA/MICCAI/ASNR).
Article | Spring 2022
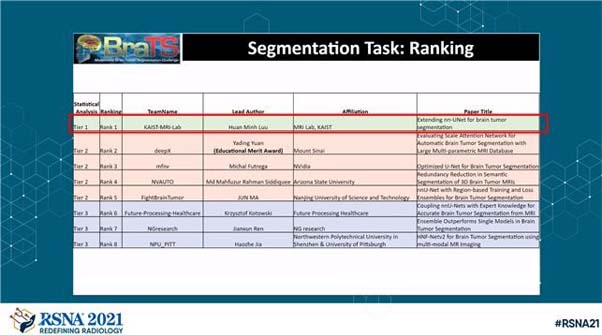
The Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge (BRATS) is a global competition held every year for the development of a deep learning network that most accurately segments brain tumors based on multi-modal MRI data. This year’s BRATS challenge is partnered with three international conferences: those of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), one of the world’s largest conferences, the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), and the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR). The competition lasted for three months and the winners were announced at the RSNA conference in November, 2021. This year, over 2200 teams from around the world entered the BRATS competition, with over 30,000 submissions. Participants included many leading companies in their fields, such as Nvidia (2018 competition winner).
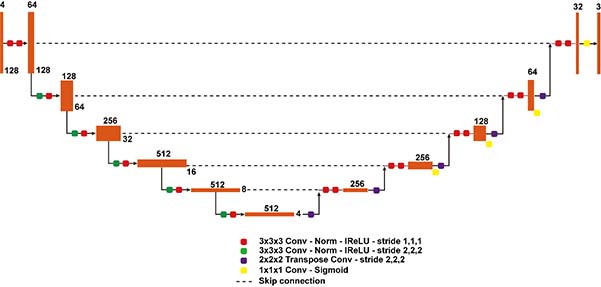
The first prize winner is Huan Minh Luu, a Ph.D. student in Professor Sung-Hong Park’s laboratory in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST. He developed a U-net-based deep learning network that improved the performance of Brain Tumor Segmentation. Specifically, more data were provided in this year’s competition than in previous years, and thus the network size in nnUNet (no-new UNet) was increased and data usage greatly improved. As the network grows, a small number of training samples are used for each training step, which can reduce performance. This issue was resolved by replacing batch normalization with group normalization: multiple models were trained with different settings and then combined for better performance.
This approach has proven very effective, outperforming other complex methods that use attention or transformer architectures. According to the organizers, there was no statistically significant difference between the submissions of the 2nd to 5th place teams, but the submission of the 1st place research team was significantly statistically superior to the others.
This is the first time that a Korean team has won first place in the BRATS challenge, and this year’s challenge is even more meaningful as it is co-hosted by three large international conferences. Korea’s competitiveness in the field of medical imaging research using deep learning has now been demonstrated internationally. It is expected that this achievement will serve as a stepping stone for future Korean researchers.
Publication: Huan Minh Luu and Sung-Hong Park. Extending nn-UNet for brain tumor segmentation. arXiv.org > eess > arXiv:2112.04653, https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04653
Most Popular

When and why do graph neural networks become powerful?
Read more
Extending the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries with water
Read more
Professor Ki-Uk Kyung’s research team develops soft shape-morphing actuator capable of rapid 3D transformations
Read more
Smart Warnings: LLM-enabled personalized driver assistance
Read more
Development of a nanoparticle supercrystal fabrication method using linker-mediated covalent bonding reactions
Read more